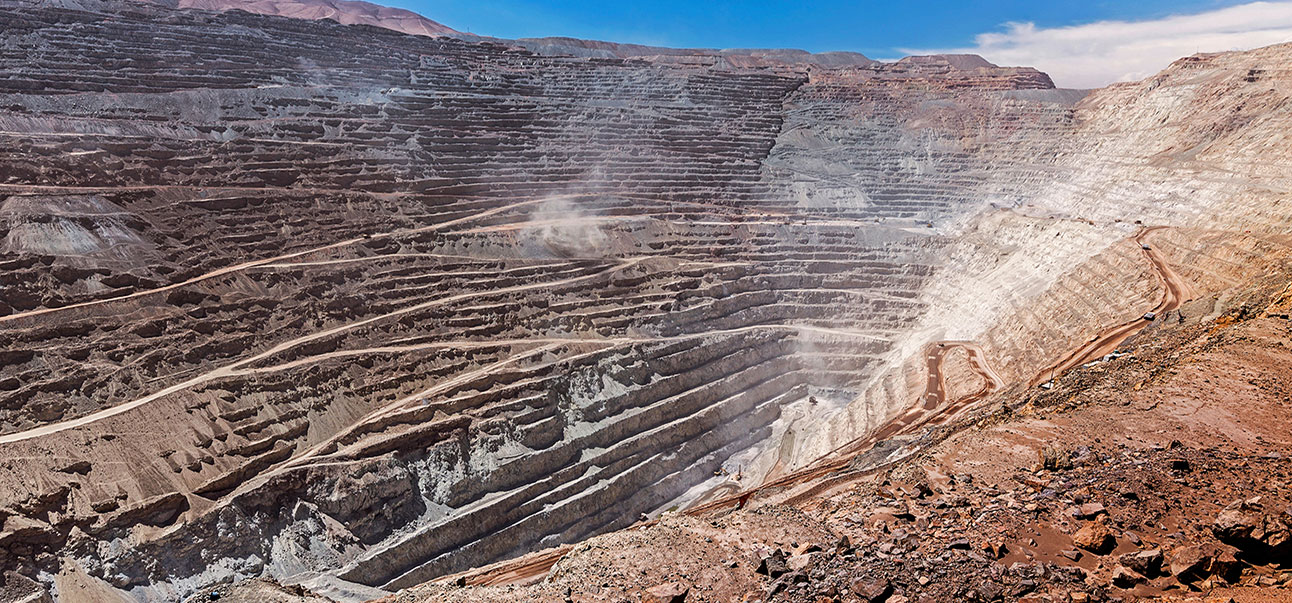
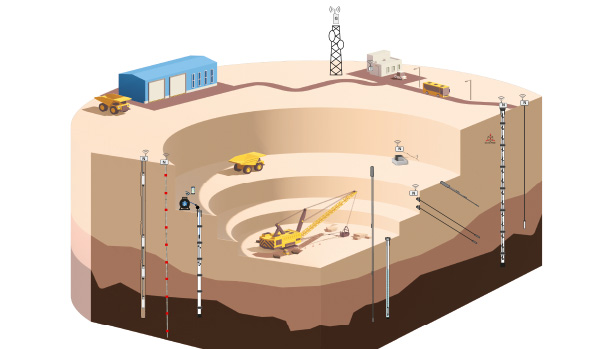
What is mines monitoring?
Mines geotechnical and structural monitoring refers to the practice of using various technologies and techniques to monitor and analyse the stability and integrity of mine structures and the surrounding rock formations. This type of monitoring is crucial to ensure the safety of workers and to prevent accidents such as mine collapses and rockfalls.
Geotechnical monitoring involves measuring and analysing the behaviour of the rock mass and soil surrounding the mine. This includes monitoring the deformation, stress, and movement of the rock mass, as well as the stability of slopes, tunnels, and other structures. Geotechnical monitoring techniques may include using geotechnical instruments such as extensometers, inclinometers, and piezometers to measure these parameters.
Structural monitoring, on the other hand, involves monitoring the condition and behaviour of mine structures such as shafts, tunnels, and buildings. This includes monitoring the integrity of the structures, detecting any signs of wear, damage, or degradation, and ensuring that they are stable and safe for workers. Structural monitoring techniques may include using sensors such as strain gauges, tiltmeters, and displacement sensors to measure the behaviour of these structures.
Overall, mines geotechnical and structural monitoring is essential to ensure the safety and stability of mining operations. By detecting any signs of instability or degradation, mining companies can take corrective action to prevent accidents and ensure the safety of their workers.

Which are the challenges in mines monitoring?
Some of the main topics and challenges in geotechnical mine monitoring include:
- Ground stability: geotechnical mine monitoring is primarily focused on monitoring ground stability to prevent ground subsidence, rockfalls, or landslides, which can endanger mine workers and damage equipment.
- Rock mass characterization: the behaviour of the rock mass surrounding a mine is critical for the safety and stability of mining operations. Geotechnical mine monitoring involves characterizing the properties of the rock mass, such as strength, deformation, and permeability, to assess its behaviour and detect any changes that could impact mining operations.
- Slope stability: mining operations often involve excavating tunnels and working underground, which can impact the stability of slopes and increase the risk of slope failure. Monitoring slope stability is essential to prevent structural failure and ensure worker safety.
Implementing an effective geotechnical monitoring system requires installing various sensors and collecting large amounts of data. Challenges include selecting the appropriate sensors, installing them correctly, and managing the data effectively to ensure its quality and reliability. Sisgeo engineers are available for any information and suggestion to select the right monitoring instrumentation set.